Insulin Resistance: Understanding the Hidden Epidemic
‘Insulin’, once thought of to be a humble hormone, is now the underlying cause of several chronic health conditions. Non-communicable diseases such as diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and some recurring cancers might have one common link – Insulin Resistance.
Wondering what’s that? Read on this blog to understand insulin resistance and its impact on overall health.
What is Insulin Resistance?
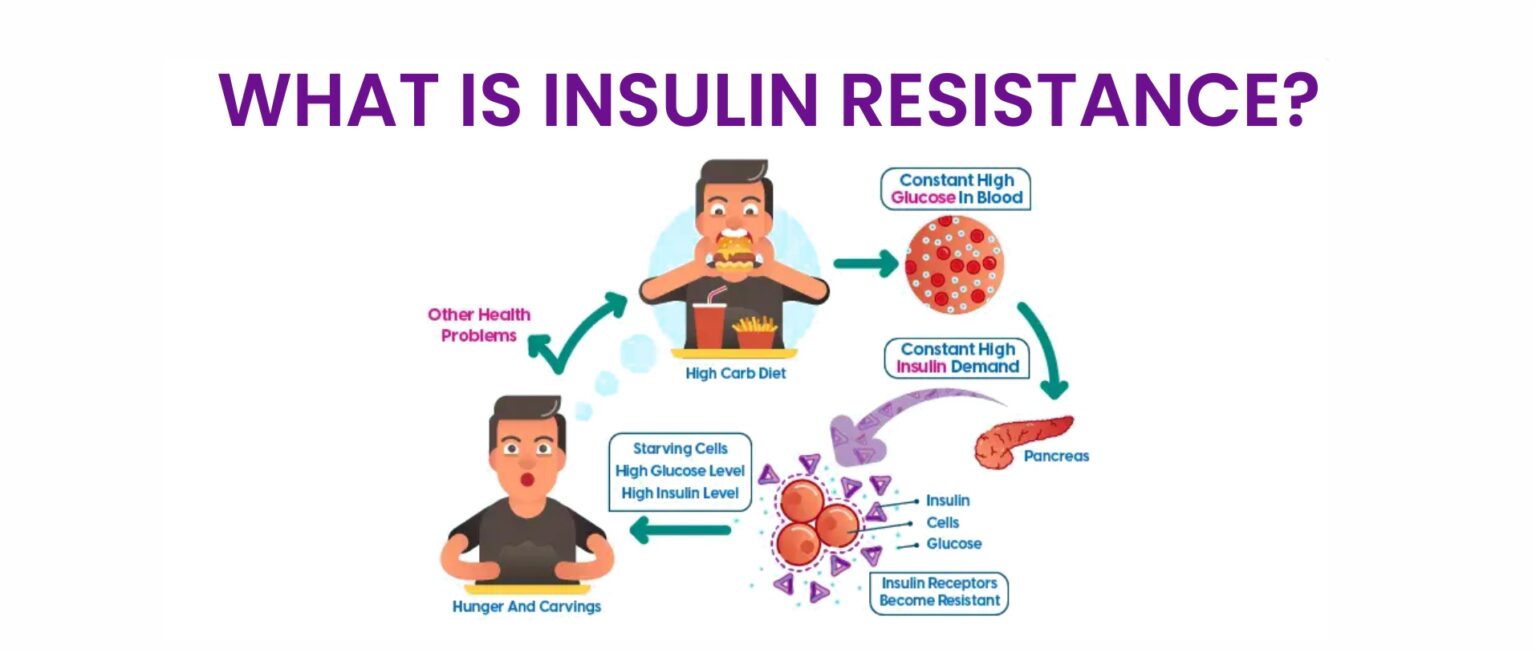
Insulin resistance, often referred to as the ‘hidden epidemic’, is a metabolic condition that affects how your body processes glucose or blood sugar. This condition occurs when cells in your muscles, fat, and liver do not respond well to insulin, a hormone made by your pancreas.
The insulin hormone is vital for controlling blood sugar levels. It allows glucose or sugar from your bloodstream to enter cells and be used for energy. When cells become insulin-resistant, they cannot absorb glucose properly, resulting in a buildup of sugar in the blood.
If not managed properly, over time, it results in the development of prediabetes and Type 2 diabetes.
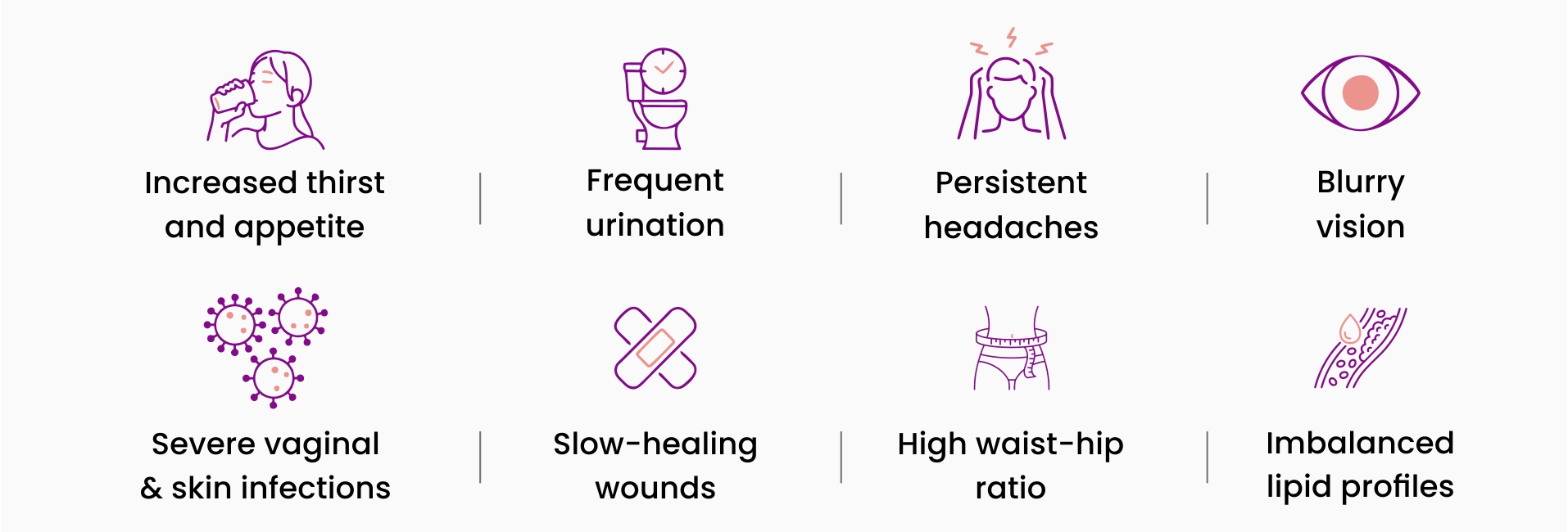
Symptoms of Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance generally does not show any symptoms until diabetes develops. A report by CDC reveals that a whopping 85% of people with prediabetes do not know that they have the condition.
You may know you have insulin resistance until you get a blood test. However, when the blood sugar levels are consistently high, you might notice:
- You are thirsty
- You are starving
- Constant urge to pee
- Blurry vision
- Extreme headaches
- Severe vaginal and skin infections
- Slow-healing wounds, cuts and sores
- High waist-hip ratio
- Uncontrolled lipid profiles
What Causes Insulin Resistance?
While it is not clear exactly what causes insulin resistance, however, certain risk factors are known to be the primary drivers. These include:
- Lifestyle factors such as sedentary lifestyle, unhealthy diet, and chronic stress.
- Genetic factors such as family history of diabetes or insulin resistance and certain ethnicities.
- Certain medical conditions like Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS in women), sleep apnoea, etc.
Additionally, other risk factors can increase your likelihood of developing insulin resistance:
- High visceral fat
- Age 45 or older
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol levels
- History of gestational diabetes
- History of heart disease such as stroke
Now that you know insulin resistance, if left unaddressed can lead to several health complications like prediabetes, type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and certain cancers, you must monitor your blood sugar levels regularly.
In case you notice that the readings are coming on the higher side, consult a healthcare professional with no further delay. Apart from this, consider making healthy lifestyle choices, opting for a fiber-rich diet, exercising for at least 150 minutes per week, maintaining weight, getting 6-8 hours of quality sleep, and managing stress effectively to prevent complications associated with insulin resistance.
If you are struggling to keep your blood sugar levels in acceptable ranges, download the hCare app to book a diet consultation with a Nutritionist.
Quick Links
Locations
- India Health Link
- IndiQube Orion, 24th Main Rd, Sector 1, HSR Layout, Bengaluru, Karnataka - 560102.
- +91 80474 85152
- info@indiahealthlink.com